RETINAL DETACHMENT SYMPTOMS
Retinal Detachment Symptoms
Retinal detachment symptoms include new floaters, flashes and loss of your peripheral vision. Most retinal detachments are called “rhegmatogenous”
retinal detachments and start with a retinal tear or retinal hole (“rhegma” is a tear or break).
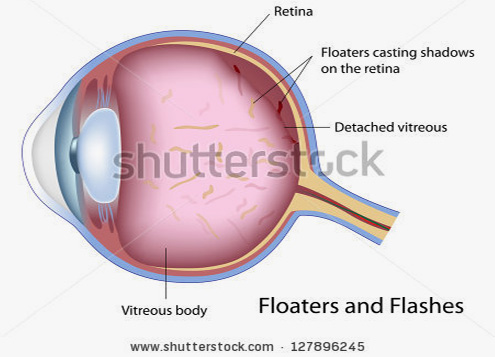
Flashes and Floaters Are Due to Vitreous Traction (Pulling on the Retina)
The vitreous, the proteinaceous gel that occupies the inside of the eye, is mostly water, yet has substance. It is very similar to a jellyfish; mostly water, but has substance. The vitreous is extremely adherent to certain parts of the retina.
Ever rub your and marvel at the patterns you see, especially in the dark? The patterns of light are a result of physical stimulation of the retina. Light is the more normal way to stimulate the retina.
Just as you can stimulate the retina with light or physical force, the vitreous can tug on the retina and cause flashes. If the retina is pulled forcefully enough, a retinal tear can develop. Sometimes, floaters are due to a retinal tear. An undiagnosed tear can lead to a retinal detachment.
Retinal tears can be caused by blunt trauma (punch), but usually are associated with a posterior vitreous detachment (PVD). Symptoms of a posterior vitreous detachment include the sudden onset of flashes and floaters; the same warning signs as a retinal detachment.
A Retinal Detachment Will Cause Loss of Peripheral Vision That Enlarges Centrally
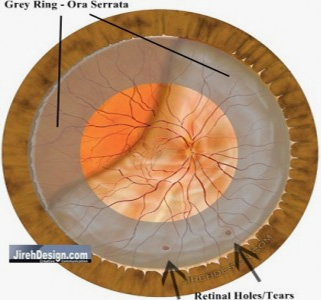
Most tears and holes are located in the anterior portion of the retina. The vitreous is most adherent here, at the ora serrata (see illustration).
The significance of this association is that a retinal tear will occur in this area causing a detachment in the peripheral retina. This, in turn, effects the peripheral vision, first. As the detachment enlarges, the central vision will be affected, last.
Flashes, Floaters and Loss of Vision – See Your Doctor!
While these are the most common symptoms of a possible tear and retinal detachment, many people may never experience symptoms.
New flashes and floaters should be examined by your doctor. Your doctor should perform a complete dilated eye exam, looking specifically for retinal tears, retinal holes or a retinal detachment.